Your Oral Medication for Melasma
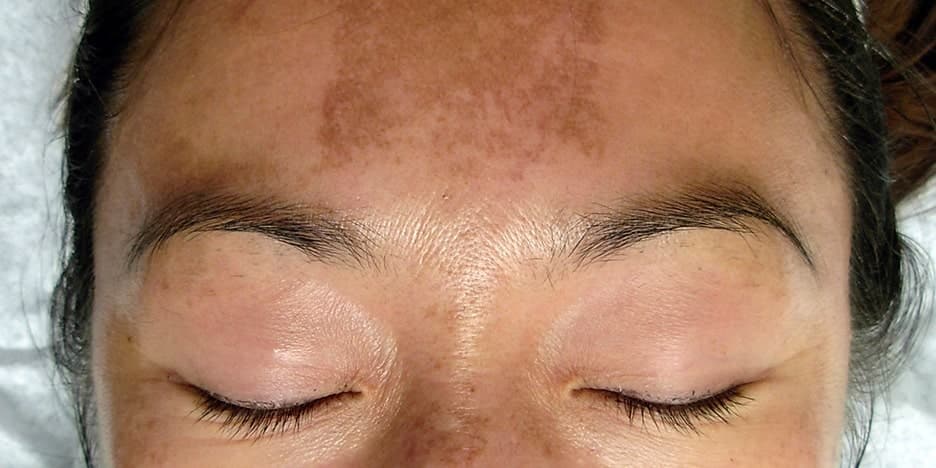

Do you suffer from patchy pigmentation on your cheeks or forehead? Have you tried many whitening products, lasers and even chemical peels without significant improvement? If you do, you may benefit from a skin pigmentation treatment in Singapore which has been shown to help with your pigmentation problem.
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes brown or greyish-brown patches, usually on areas exposed to the sun – most often the cheeks, forehead, nose, upper lip, and chin.
Melasma is more common in women, especially those with medium to darker skin tones, and often develops during periods of hormonal changes, such as pregnancy, oral contraceptive use, or hormone therapy.
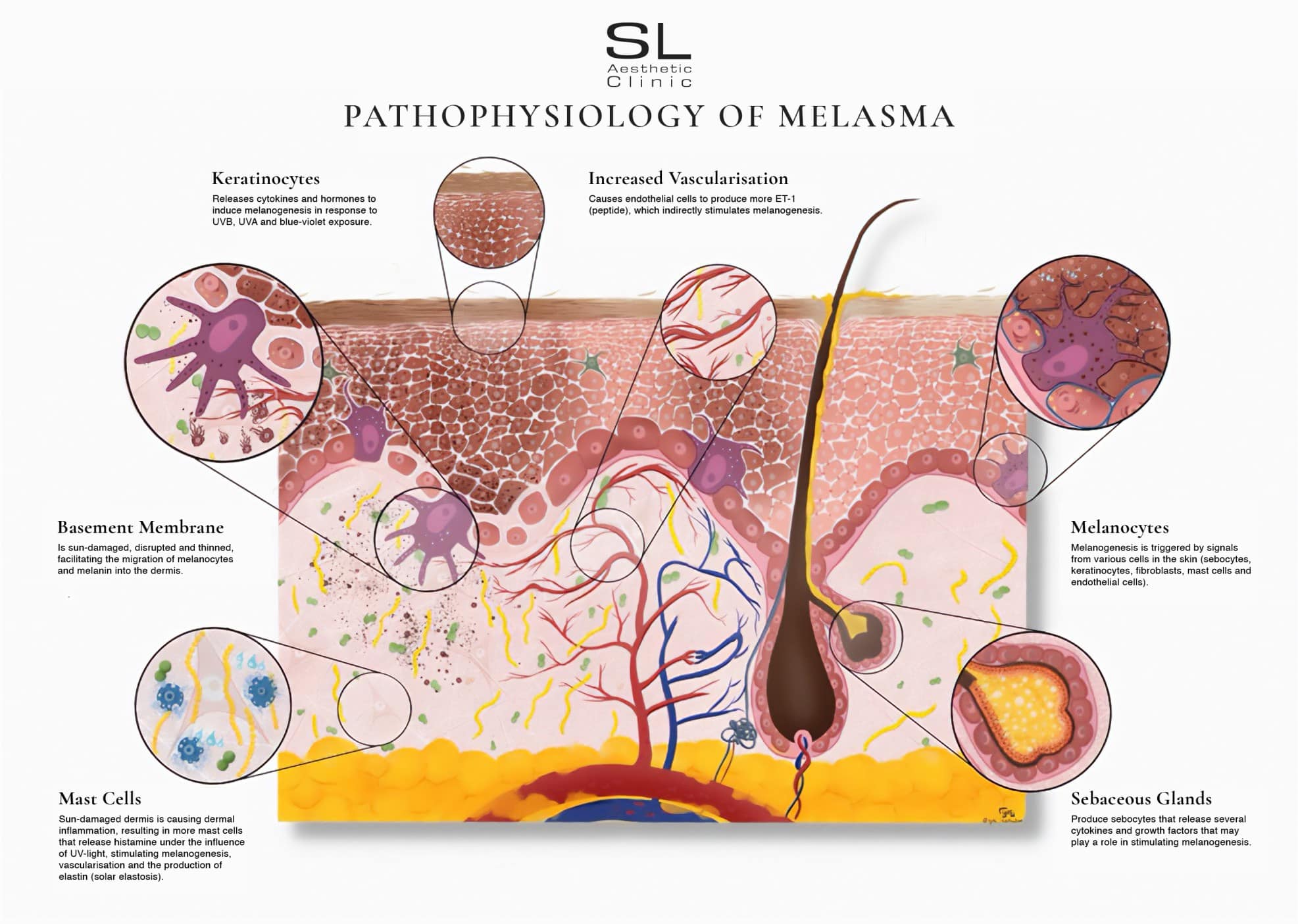
Melasma occurs when melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin, become overactive and produce too much melanin (the pigment that gives skin its colour).
When your skin is exposed to sunlight, heat, or hormonal changes, your skin cells (called keratinocytes) send signals that trigger melanin-producing cells (melanocytes) to make more pigment. Over time, these signals become too active, leading to dark patches on the skin.
Other changes happen too:
More blood vessels form in the area, which can fuel more pigmentation.
Mast cells, part of your immune system, release substances that increase inflammation and pigment.
Oil glands (sebaceous glands) may also play a role by reacting to hormones and heat.
The skin’s foundation layer (basement membrane) can become damaged, letting pigment sink deeper and making melasma harder to treat.
So even though melasma looks like just dark patches, it’s actually a mix of pigmentation, inflammation, hormonal activity, and structural skin changes. Other factors that trigger melasma include genetics, skincare products and stress.
Melasma usually presents as symmetrical, brownish patches on sun-exposed areas of the skin. The most affected regions include the:
In some cases, melasma can also affect the neck and forearms. The skin pigmentation is not raised or inflamed but can vary in intensity and may darken over time without proper treatment or protection from sun exposure.
Over-the-counter whitening products used to lighten pigmentation show limited results on Melasma, and topical medications and medical laser treatments on their own can sometimes produce marginal improvements. Melasma is also challenging to treat as it tends to recur with time and sun exposure.
Fortunately, researchers at Singapore’s National Skin Centre found that the Oral Medication for Pigmentation, used in treating heavy menstrual periods, showed significant lightening of Melasma in over 90 per cent of patients it studied.
Oral Medication for Pigmentation is proposed to reduce pigmentation by inhibiting UV-induced melanocyte (cells that produce melanin) activation. Oral Medication for Pigmentation can also stabilise the blood vessels and reduce skin inflammation, a contributing factor in melasma.
Side effects are minimal with the medication, it is generally suitable for those in good health. Contraindications include those with a personal/family history of blood disorders, pregnant women, and ladies on oral contraceptive pills.
When deciding between Oral Medication for Pigmentation and topical treatments for pigmentation, it’s important to consider the pros and cons of each.
Besides oral and topical medications, several other treatments can be effective in managing melasma, including:
Do you suffer from patchy pigmentation and want to know if you’ll benefit from this treatment? Speak to any of our doctors at SL Aesthetic Clinic and we’ll be happy to advise on the pigmentation removal treatments most suited for you.
The most commonly prescribed oral medications for melasma include:
These medications can be used on their own or in combination with other treatments to improve pigmentation issues.
Results from oral treatments typically take about 4 to 8 weeks to become noticeable. However, it’s essential to continue the treatment for several months to maintain the effects and prevent recurrence.
Oral medications for melasma may not be suitable for:
While generally well-tolerated, oral medications can have side effects, including:
Please consult your doctor before starting any oral medication for melasma.
Yes, combining oral medications with topical treatments often leads to better outcomes for melasma patients. This combination addresses pigmentation both on the surface and internally, providing a more comprehensive approach.
Oral medications can complement cosmetic anti-pigmentation treatments like chemical peels, microneedling, or laser therapy. These combined approaches often lead to faster and more significant improvements in skin pigmentation, though they should be done under the supervision of a doctor to minimise risks.
Like what you read? Share them!